Lung base means a process at the bottom of the lungs. The lungs have left upper and lower lobes and right upper, middle, and lower lobes on the right. When we say lung base, we mean the bottom of the lower lobes on both sides. This is a common location for abnormalities. We will often see an abnormality described as being at the lung base in a
Imaging the chest (Chapter 1) – Radiology for Anaesthesia and Intensive Care
Interstitial Lung Disease refers to a large group of lung disorders that cause inflammation or scarring in the lung tissue. The term “interstitial” refers to the area that surrounds the airsacs (alveoli) of the lung. This interstitial space is where the oxygen that you breathe in moves across the wall of the alveoli and into the small blood
Source Image: globaltb.njms.rutgers.edu
Download Image
Apr 25, 2023Interstitial (in-tur-STISH-ul) lung disease describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream. Interstitial lung disease can be caused by long-term exposure to

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
3. Basic patterns in lung disease | Radiology Key Hyperinflated Lungs. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their usual size due to air being trapped inside. It’s common in people with COPD and other respiratory conditions. It causes symptoms like difficulty inhaling and shortness of breath. Treatment involves medication, breathing exercises or oxygen therapy.
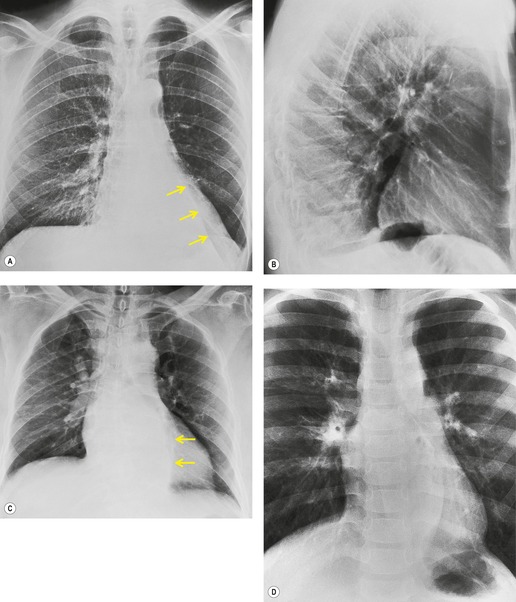
Source Image: radiologykey.com
Download Image
Crowding Of Basal Lung Markings Meaning
Hyperinflated Lungs. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their usual size due to air being trapped inside. It’s common in people with COPD and other respiratory conditions. It causes symptoms like difficulty inhaling and shortness of breath. Treatment involves medication, breathing exercises or oxygen therapy. The Clinical Challenge. Section: An 84-year-old man with a long history of asthma and gastroesophageal reflux presented to his primary care physician with progressive dyspnea on exertion and cough. His primary care physician initiated treatment with an inhaled bronchodilator and a proton pump inhibitor; however, the dyspnea and cough persisted.
3. Basic patterns in lung disease | Radiology Key
Radiology 31 years experience. Lung base unexpanded: The diaphragm is a thin membrane like muscle which stretches downward to expand the lungs. when it relaxes it moves upward and lungs compress. someti… Read More. Created for people with ongoing healthcare needs but benefits everyone. Respiratory pathology | PPT

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
What do mildly increased lung markings mean? – Quora Radiology 31 years experience. Lung base unexpanded: The diaphragm is a thin membrane like muscle which stretches downward to expand the lungs. when it relaxes it moves upward and lungs compress. someti… Read More. Created for people with ongoing healthcare needs but benefits everyone.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Imaging the chest (Chapter 1) – Radiology for Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Lung base means a process at the bottom of the lungs. The lungs have left upper and lower lobes and right upper, middle, and lower lobes on the right. When we say lung base, we mean the bottom of the lower lobes on both sides. This is a common location for abnormalities. We will often see an abnormality described as being at the lung base in a
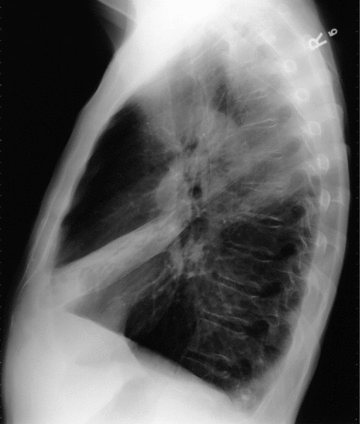
Source Image: cambridge.org
Download Image
3. Basic patterns in lung disease | Radiology Key Apr 25, 2023Interstitial (in-tur-STISH-ul) lung disease describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream. Interstitial lung disease can be caused by long-term exposure to
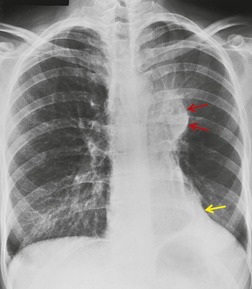
Source Image: radiologykey.com
Download Image
Image: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (Chest X-ray) – MSD Manual Professional Edition Oct 17, 2023Common Causes. Infection: Lung infections, such as pneumonia, can cause an increase in bronchovascular markings due to inflammation. Allergies: Allergic reactions may lead to temporary thickening of bronchovascular markings. Chronic Lung Conditions: Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can result in pronounced markings.

Source Image: msdmanuals.com
Download Image
Radiology Rounds – 6/14/22 | PulmPEEPs Hyperinflated Lungs. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their usual size due to air being trapped inside. It’s common in people with COPD and other respiratory conditions. It causes symptoms like difficulty inhaling and shortness of breath. Treatment involves medication, breathing exercises or oxygen therapy.

Source Image: pulmpeeps.com
Download Image
Bronchopulmonary segments: Anatomy and clinical aspects | Kenhub The Clinical Challenge. Section: An 84-year-old man with a long history of asthma and gastroesophageal reflux presented to his primary care physician with progressive dyspnea on exertion and cough. His primary care physician initiated treatment with an inhaled bronchodilator and a proton pump inhibitor; however, the dyspnea and cough persisted.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/medial-basal-segment-of-right-lung/ZLSTwixLbO9h74Zt5Reg_Medial_basal.png)
Source Image: kenhub.com
Download Image
What do mildly increased lung markings mean? – Quora
Bronchopulmonary segments: Anatomy and clinical aspects | Kenhub Interstitial Lung Disease refers to a large group of lung disorders that cause inflammation or scarring in the lung tissue. The term “interstitial” refers to the area that surrounds the airsacs (alveoli) of the lung. This interstitial space is where the oxygen that you breathe in moves across the wall of the alveoli and into the small blood
3. Basic patterns in lung disease | Radiology Key Radiology Rounds – 6/14/22 | PulmPEEPs Oct 17, 2023Common Causes. Infection: Lung infections, such as pneumonia, can cause an increase in bronchovascular markings due to inflammation. Allergies: Allergic reactions may lead to temporary thickening of bronchovascular markings. Chronic Lung Conditions: Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can result in pronounced markings.